Integrated Pest Management (IPM) in onion
Integrated pest management (IPM) plays a crucial role in ensuring the health and productivity of onion crops due to the presence of various pests and diseases.
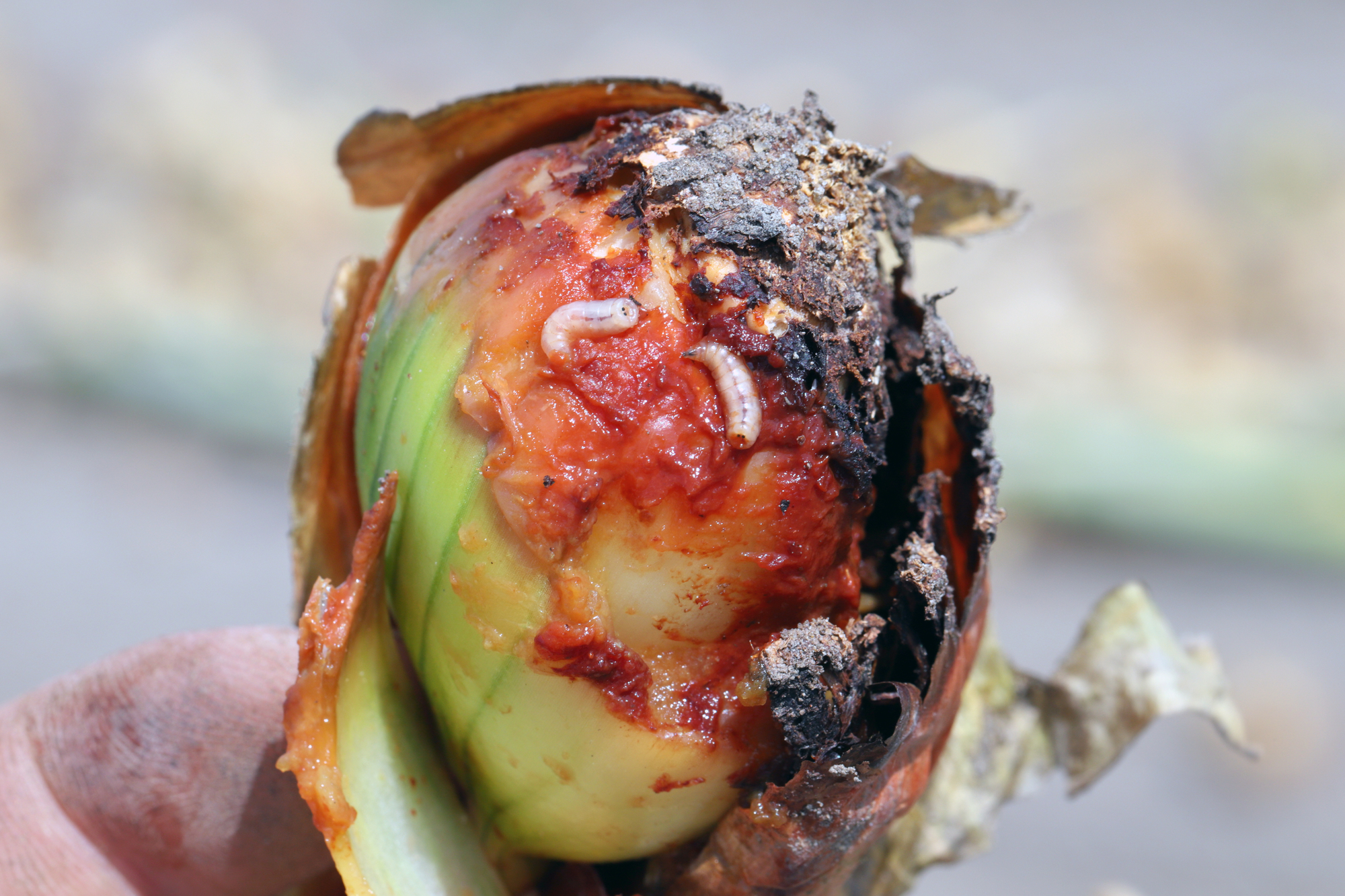
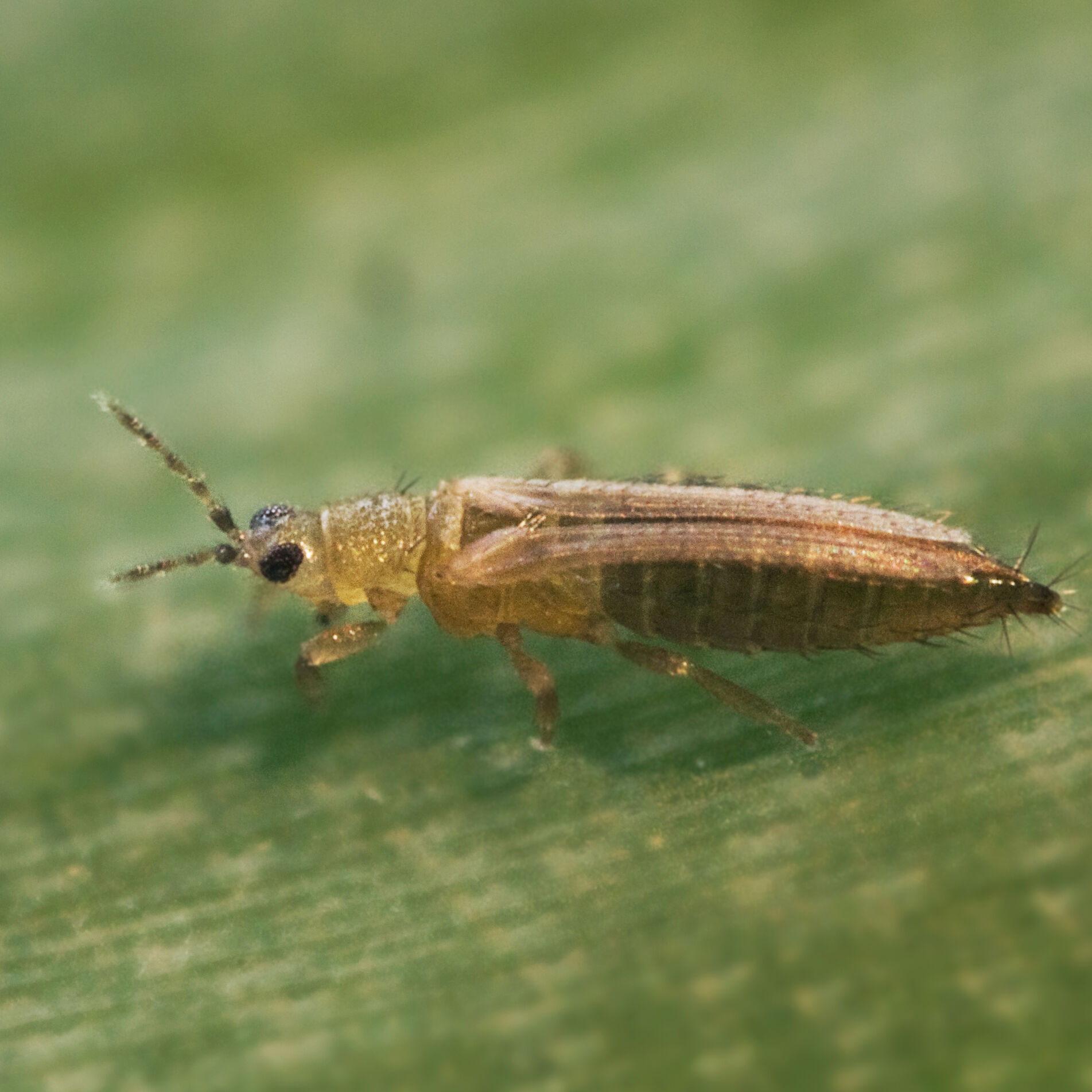
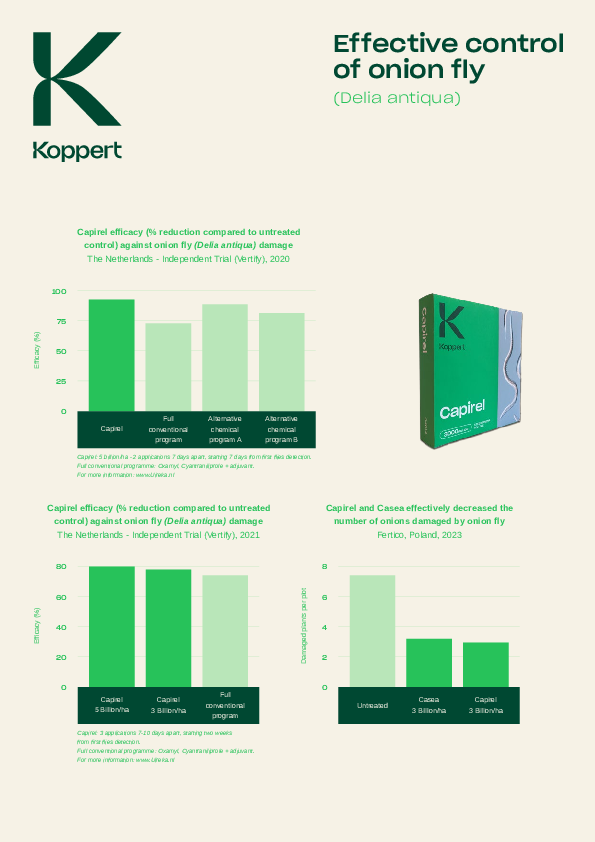
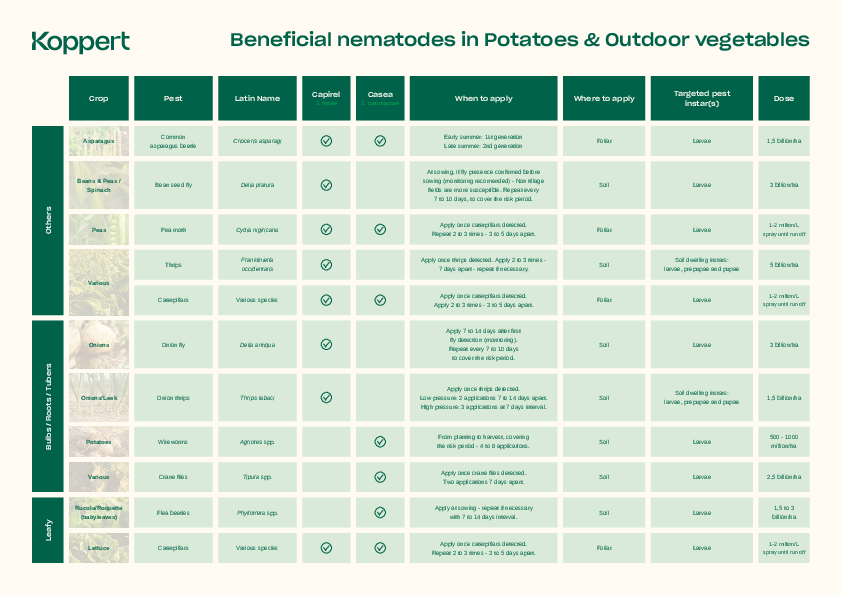
Common pests that occur in onion are onion fly, bean seed fly, onion thrips, stone-leek leafminer, and many more. These pests can cause significant damage to the plants, leading to reduced yields and compromised vegetable quality.
In addition to pests, onion crops are also susceptible to several diseases, including bacterial diseases, Botrytis, Fusarium, downy mildew, and pink root. These diseases can weaken the plants, stunt their growth, and cause severe damage to both foliage and vegetables, if not properly managed.
Implementing IPM strategies is crucial for effectively controlling and reducing the impacts of these pests and diseases. By combining various techniques such as cultural practices, biological control agents, resistant cultivars and targeted pesticide applications, growers can maintain a balance between pest control and environmental sustainability, while safeguarding the health and yield of their onion crops.
Using IPM strategies not only minimizes the use of harmful chemical pesticides, but also promotes the long-term resilience of the onion crops, ensuring the production of high-quality onions for consumers.